| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- JSP
- 부트스트랩
- Oracle SQL
- sql developer
- ||
- 모조칼럼
- JavaScript
- jQuery
- distinct
- 과정평가형
- Java
- 답변형 게시판
- github
- 제약조건
- oracle
- HTML
- HTTP Status 404
- 이클립스
- Bootstrap
- git
- group by
- Oracle DB
- alias
- 성적프로그램
- HTTP Status 500
- 한글 인코딩
- rownum
- tomcat
- CRUD
- SQL
Archives
초급의 끄적거림
[JAVA] 반복문 (While / For문) / 배열 Array 본문
* oop0521
1. while 반복문
1-1) 형식
while ( 조건 ){ while이 true이면 수행 }, 조건이라는 말이 나오면 boolean 형태
<무한 루프>
while (true){ }
- 아무 조건 없이 처음부터 true를 줬기 때문에 계속 반복
for(;;) { }
1-2) 연습
//무한 루프
int a=1;
while(true){ //만약에 while(true) 는 무한루프에 해당
System.out.println("SEOUL");
if(a==3){
break; //반복문 탈출 - 딱 SEOUL이 한 번 나오게 됨, 무한루프였어도 3번에서 탈출
}
a++;
}//while end
/*
while(true) SEOUL if(1==3) a=1+1
while(true) SEOUL if(2==3) a=2+1
while(true) SEOUL if(3==3) a=3+1
*/int a=1;
while(a<=3){ //초기값 a=1 이나 증감의 값인 a++의 위치가 따로 정해져 있지않기 때문에 알아서 정해야함
System.out.println("JAVA");
a++; // 만약 정해주지 않으면 무한루프가 생성됨. a가 3에 도달하지 않고 계속 돌기 때문.
}//while end
/*
while (1<=3) JAVA a=1+1
while (2<=3) JAVA a=2+1
while (3<=3) JAVA a=3+1
while (4<=3) X
*/
2. do~while 문
2-1) 형식
do{
조건이 true이면 수행
} while ( 조건 );
int c=1;
do {
System.out.println("JAVA");
c++
} while (c<=3); //while이 명령어 순서상 뒤에 있음. 초기값이 안 맞으면 while이나 for 문이랑 비교했을때 차이 발생
/*
JAVA a=1
JAVA a=1+1 while(2<=3)
JAVA a=2+1 while(3<=3)
X a=3+1 while(4<=3)
*/
// do~while 문은 ☆조건의 참, 거짓과 상관없이 무조건 한 번은 수행 된다.☆
int b=5;
do{
System.out.println("SEOUL"); //SEOUL을 만나서 일단 SEOUL을 한 번 찍음
b=b+1 //b=5+1 while(6<=3), 나중에 물어보기 때문에 일단 SEOUL은 한 번 찍힌 후 범위에 해당이 없으면 그대로 끝
} while (b<=3);
System.out.println(b); //위 같은 과정 때문에 b=6이 됨
2-2) 연습

// 문제1)
// x값이 10으로부터 x를 여러번 뺀 후 결과가 음수가 되면 x를 몇 번 뺐는가를 구하시오
//10-3= 7, 7-3=4, 4-3=1, 1-3=-2, -3을 4번 수행함. 4번을 뺀 것
/*
int x=3, y=10;
int count = 0;
while(x>0){
y=y-x;
count=count+1;
if(y<0){
break;
}//break end
}//while end
System.out.println(count+"개");
*/
// 강사님 방법
int x=3;
int count = 0;
int su=10;
while(true){
count++;
su=su-x;
if(su<0){
break;
}
}
System.out.println(count + "개");
/* 문제1) 분석
while(true)
{ count=0+1
su=10-3
if(7<0)}
while(true)
{count=1+1
su=7-3
if(4<0)}
*/
// 문제2) - double 형 형태
// 어느 달팽이는 낮에는 3cm 올라가고 밤에는 2.5cm 내려온다고 할 때 달팽이가 13cm의 나무 꼭대기에 올라가려면 며칠이 걸리는지 구하시오
int day=0; //며칠
double snail=0.0; //달팽이
while(true){//if까지 들어가서 다시 while까지 하고 if하고 다시 while부터 시작
day++;
snail = snail+3.0;
if(snail>=13.0){
break;
} else {
snail = snail - 2.5;
}
}//while end
System.out.println(day+ "일");
/*
문제2) 분석
while(true){ snail = 0+3.0
if(0.5>=13.0)} else {3.0-2.5= 0.5}
while(true){snail = 0.5+3.0
if(3.5>=13.0) else {3.5-2.5=1}
*/
3. For 문 (이중 반복문 - 중첩)
3-1) 반복문
for(int a=1; a<=2; a++){
System.out.println("JAVA");
for(int b=1;b<=3; b++) {
System.out.println("SEOUL");
}//for end
}//for end
/*
a=1, 1<=2 - JAVA
b=1 1<=3 SEOUL
2<=3 SEOUL
3<=3 SEOUL
a=2, 2<=2 - JAVA
b=1 1<=3 SEOUL
2<=3 SEOUL
3<=3 SEOUL
*/
//2단~9단 출력
for(int a=2; a<=9; a++){
System.out.println(a+"단");
for(int b=1; b<=9; b++){
System.out.println(a+"*"+b+"*"+"="+(a*b));
}//for end
}//for end
3-2) 반복문을 사용하여 도형만들기
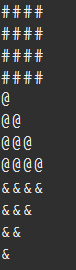
//반복문을 이용해서 사각형만들기
//→ 등수 구하는 알고리즘
for(int a=1; a<=4; a++){//a가 4번 반복
for(int b=1; b<=4; b++){
System.out.print("#");
}//for end
System.out.println();
}//for end
//반복문 이용해서 왼쪽 아래 직각 삼각형 만들기 - 회전수 증가, 예) 로또번호
for(int a=1; a<=4; a++){//a가 4번 반복
for(int b=1; b<=a; b++){
System.out.print("@");
}//for end
System.out.println();
}//for end
//반복문 이용해서 왼쪽 위 직각삼각형 만들기 2 - 회전수 감소, 예) 정렬 (bubble sort)
for(int a=4; a>=1; a--){//a가 4번 반복
for(int b=1; b<=a; b++){
System.out.print("&");
}//for end
System.out.println();
}//for end
3-3) 반복문 연습
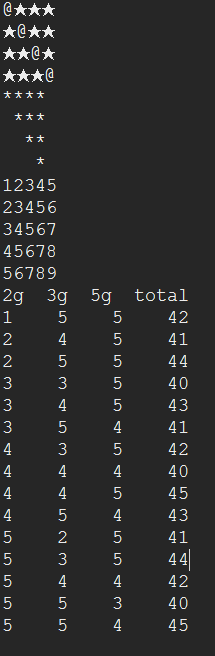
//문1)
/* @★★★
★@★★
★★@★
★★★@
*/
for(int a=1; a<=4; a++){
for(int b=1; b<=4; b++){
if(a==b){
System.out.print("@");
}else{
System.out.print("★");
}
}
}//for end
//문2)
/*
****
***
**
*
*/
for(int s=1; s<=4; s++){
for(int m=1; m<=4; m++){
System.out.print("*");
}else{System.out.print(" ");}
}
}//for end
//문3)
/*
12345
23456
34567
45678
56789
*/
for(int a=0; a<5; a++){
for(int b=a+1; b<=a+5; b++){
System.out.print(b);
}
System.out.println();
}//for end
//문4)
// 2g, 3g, 5g짜리 추가 각각 5개씩 있을 떄 세 가지의 추의 조합으로 무게가 40~45g 사이일 때 각 추의 갯수와 무게를 출력하는 프로그램
/* 출력결과
2g 3g 5g total
*
*/
System.out.println("2g 3g 5g total");
int hap=0;
for(int a=1; a<=5; a++){ // 2g추
for(int b=1; b<=5; b++){ // 3g추
for(int c=1; c<=5; c++){ // 5g추
hap= (a*2)+(b*3)+(c*5);
if(hap>=40&&hap<=45){
System.out.println(a+" "+b+" "+c+" "+hap);
}//if end
}//for end
}//for end
}//for end
4. Array 배열
- 반복문과 같이 오면 편하기 때문에 완전 절친, 반복문으로 쓰기에 적합한 규칙성을 가지고 있기 때문
- 동일한 자료형 값의 집합
- 순서, 색인, index
요소 element
- 1차원 : 열 구성, 자바에서 많이 쓰임
- 2차원 : 행과 열 구성
- 3차원 : 자바에는 없는 개념
- 열, 칸, column
- 행, 줄 row
- new 연산자로 메모리를 할당한 후 사용한다
: ex) int[] aver=new int[5]; 일 때 5만큼의 메모리를 할당해서 새로운 자리를 만들라는 의미
4-1) 연습
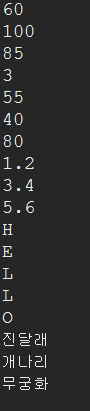
//4byte * 3 → 12byte 메모리 할당
int [] kor = new int [3];
kor[0]=60; //배열의 인덱스는 0부터 시작
kor[1]=100; //배열의 인덱스는 1씩 증가
kor[2]=85;
System.out.println(kor[0]);
System.out.println(kor[1]);
System.out.println(kor[2]);
//kor 배열 요소의 개수
System.out.println(kor.length); //3 (.length : 칸이 몇 칸인지를 알려주는 것, 자바 문자열의 길이)
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int [] eng={55, 40, 80}; //,를 중심으로 3개인 것을 확인하고 12byte 메모리 할당
int size=eng.length; //3
for(int a=0; a<size; a++){
System.out.println(eng[a]); //인덱스를 구하는 반복문이기 때문에 [a]를 설정하고 eng의 인덱스이기 때문에 (eng[a]) 가 됨
}//for end
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
double[] aver={1.2, 3.4, 5.6};
for(int a=0; a<aver.length; a++){ //a는 [0],[1],[2] ~ 가 되기 때문에 aver.length의 개수가 3개니까 a<3가 되는 것
System.out.println(aver[a]);
}//for end
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
char [] ch={'H','E','L','L','O'};
for(int a=0; a<ch.length; a++){
System.out.println(ch[a]);
}//for end
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
String [] name={"진달래", "개나리", "무궁화"};
for(int a=0; a<name.length; a++){
System.out.println(name[a]);
}//for end
5. 연습
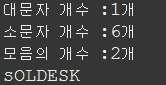
// 1차원 문자형 배열
/*
char[] ch={'S','o','l','d','e','s','k'};
int size=ch.length;
for(int idx=0; idx<size; idx++){
System.out.print(ch[idx]);
}//for end
System.out.println();
*/
//---------------------------for 문장에 다 넣어서 할 수 있는 방법 연구할 것-------------------------------------------------------------
//문1) 대문자, 소문자의 갯수를 각각 구하시오
//반복문 하나에 몰아서 풀 수 있다.
char[] ch={'S','o','l','d','e','s','k'};
int size=ch.length;
/*
int count=0;
int count1=0;
for(int idx=0; idx<size; idx++){
if(ch[idx]>='A'&&ch[idx]<='Z'){
count=count+1;
System.out.print(count+"개");
}
}//for end
*/
int upper=0, lower=0, mo=0;
for(int idx=0; idx<size; idx++){
if(ch[idx]>='A'&&ch[idx]<='Z'){ // ch 배열의 [idx] - 0, 1, 2, 3~~ 를 구하는 것이기 때문에 ch[idx]
upper++;
}//if end
if(ch[idx]>='a'&&ch[idx]<='z'){
lower++;
}//if end
}//for end
System.out.println("대문자 개수 :" + upper + "개");
System.out.println("소문자 개수 :" + lower + "개");
//문2) 모음의 갯수를 구하시오 -1) mo와 switch를 이용해서 2) 노가다
for(int idx=0; idx<size; idx++){
if(ch[idx]>='a'&&ch[idx]<='z'){
lower++;
switch(ch[idx]){
case 'a':
case 'e':
case 'i':
case 'o':
case 'u': mo++; }
}//if end
}//for end
/* <내 방식>
for(int idx=0; idx<size;idx++){
if(ch[idx]=='a'||ch[idx]=='e'||ch[idx]=='i'||ch[idx]=='o'||ch[idx]=='u'){
mo++;
}//if end
}//for end
*/
System.out.println("모음의 개수 :" + mo + "개");
//문3) 대문자와 소문자를 서로 바꿔서 출력하시오 → sOLDESK
/* <내 방법>
for(int idx=0; idx<size;idx++){
char alpha=(ch[idx]>='A' && ch[idx]<='Z') ? (char)(ch[idx]+32) : (char)(ch[idx]-32);
System.out.print(alpha);
}//for end
*/
// 강사님 방법
for(int idx=0; idx<size; idx++){
if(ch[idx]>='A'&&ch[idx]<='Z'){ // ch 배열의 [idx] - 0, 1, 2, 3~~ 를 구하는 것이기 때문에 ch[idx]
System.out.print((char)(ch[idx]+32));
}//if end
else if(ch[idx]>='a'&&ch[idx]<='z'){
System.out.print((char)(ch[idx]-32));
} else{
System.out.println(ch[idx]); // 대문자도, 소문자도 아니고 이도 저도 아니면 출력할 것
}//if end
}//for end'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Base64] base64 암호화 복호화 (0) | 2019.11.28 |
|---|---|
| [Ecilpse 오류] save could not be completed (0) | 2019.11.25 |
| [JAVA] 임시 비밀번호 생성 소스 (0) | 2019.09.25 |
| [JAVA] 반복문 (for / 무한루프 / break / continue) (0) | 2019.09.10 |
| [JAVA] Eclipse 단축키 (0) | 2019.08.29 |
Comments


