| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- sql developer
- jQuery
- 과정평가형
- HTTP Status 404
- 답변형 게시판
- oracle
- 이클립스
- distinct
- JavaScript
- CRUD
- group by
- SQL
- 모조칼럼
- 한글 인코딩
- HTTP Status 500
- tomcat
- ||
- 부트스트랩
- 성적프로그램
- git
- Bootstrap
- Oracle SQL
- Oracle DB
- Java
- JSP
- alias
- rownum
- HTML
- 제약조건
- github
초급의 끄적거림
[SQL] Index 본문
[Index (색인)]
⊙ 주로 개념 위주로 알아줄 것.
⊙ 데이터를 빠르게 찾을 수 있는 수단
⊙ 테이블에 대한 조회 속도를 높여주는 자료구조
⊙ Primary Key, Unique 제약조건은 자동으로 인덱스 생성이 된다
⊙ 인덱스 기본 형식
· 인덱스 생성 : create index 인덱스명
· 인덱스 삭제 : drop index 인덱스명
· 인덱스 수정 : alter index 인덱스명
⊙ 인덱스 방식
· full scan : 처음부터 끝가지 일일이 검사하는 방법 (전수조사)
· index range scan : 이름이 여러 개인 경우 목차를 찾아서 페이지를 찾아감
: 훨씬 빠르되 별도의 메모리가 필요
· index unique scan : 학번은 1개만 존재하듯이 '유일한 값'
⊙ 사용할 c_emp 테이블 생성
select * from c_emp;
drop table c_emp;
create table c_emp(
id number(5)
,name varchar2(25)
,salary number(7, 2)
,phone varchar2(15)
,dept_id number(7)
);
insert into c_emp(id,name) values (10,'kim');
insert into c_emp(id,name) values (20,'park');
insert into c_emp(id,name) values (30,'hong');
⊙ c_emp 테이블을 활용한 인덱스 확인
1) 인덱스 생성 전
- 이름이 '홍'인 사람

|
select * from c_emp where name='hong'; |
- F10을 이용하여 실행계획 보기 (커서 위치 중요) : 잘 안되면 전체 블록 후 F10

2) 인덱스 생성 후
- c_emp_name_index 를 만들고 F10

|
create c_emp_name_index on c_emp(name); + F10 |
⊙ emp4 테이블을 활용한 인덱스 확인
1) emp4 테이블 생성
create table emp4 (
no number primary key
,name varchar2(10)
,sal number
);
→ no 의 primary key는 자동으로 인덱스가 생성되어 정렬됨
- 인덱스 목록보기
select * from user_indexes;

- F10을 이용한 emp4의 실행계획보기
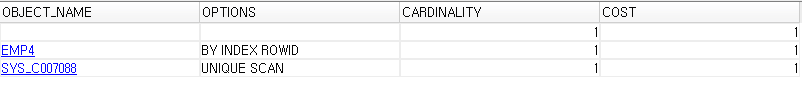
⊙ 예) 테스트용 레코드 100만건 입력
- PL/SQL (Procedural Language) 프로시저 → 절차적인 데이터베이스 프로그래밍 언어
1) emp3 테이블 만들기
create table emp3(
no number
,name varchar2(10)
,sal number
);
2) declare 선언문
|
declare i number := 1; - i 변수에 1 대입 ( := ) 연산자 name varchar2(20) :='kim'; sal number := 0; begin while i<=1000000 loop if i mod 2 = 0 then - mod : 나눠서 나머지가 남는 연산자 namve := 'kim' || to_char(i); sal := 300; elsif i mod 3 = 0 then - java와 다르게 else if 가 아닌 elsif를 사용 name := 'park' || to_char(i); sal := 400; elsif i mod 5 = 0 then name := 'hong' || to_char(i); sal := 500; else name := 'shin' || to_char(i); sal := 250; end if;
insert into emp3(no, name, sal) values (i, name, sal): end loop; end; / - 종결문자 |
- select count (*) from emp3;

[모조칼럼]
⊙ rowid 행의 주소값
⊙ rownum 행번호

|
select * from emp3 where rownum>=1 and rownum<=10; |
⊙ 문제) name 칼럼을 기준으로 인덱스 생성한 후 name 칼럼에서 조회하고 F10 계획 결과 확인하세요
1) 인덱스를 사용하지 않은 경우

|
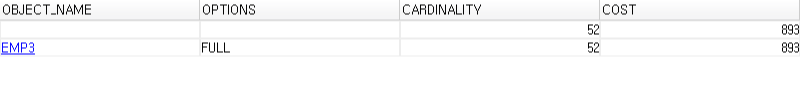
select * from emp3 where name='kim466'; |
- f10 적용 : full scan, cost 893
2) 인덱스 사용
|
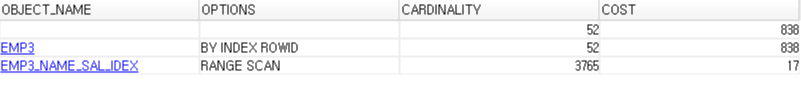
create index emp3_name_index on emp3(name); |
|
select * from emp3 where name ='kim466'; |

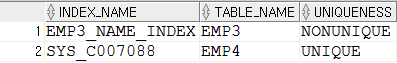
- 테이블 이름이 EMP3, EMP4인 경우를 찾아내는 방법
|
select index_name, table_name, uniqueness from user_indexes where table_name in('EMP3', 'EMP4'); |
<이름과 급여를 기준으로 인덱스 페이지만듦>
- 숫자가 466일 때

|
select * from emp3 where no=466; |
- 이름이 kim466으로 찾기
|
select * from emp3 where name='kim466'; |
- 급여가 200보다 클 때

|
select * from emp3 where sal>200; |
- 이름이 kim466 이고 급여가 200보다 클 때

|
select * from emp3 where name='kim466' and sal>200; |
'DB > Oracle' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SQL] case when ~ then end 구문 / decode() 함수 (0) | 2019.07.25 |
|---|---|
| [SQL] join 1 (0) | 2019.07.24 |
| [SQL] View (0) | 2019.07.23 |
| [SQL] 서브쿼리 (Sub Query) (0) | 2019.07.23 |
| [SQL] group 외 예제 (0) | 2019.07.23 |




